

- PC 4 PIN FAN PINOUT DRIVER
- PC 4 PIN FAN PINOUT FULL
- PC 4 PIN FAN PINOUT PC
- PC 4 PIN FAN PINOUT SERIES
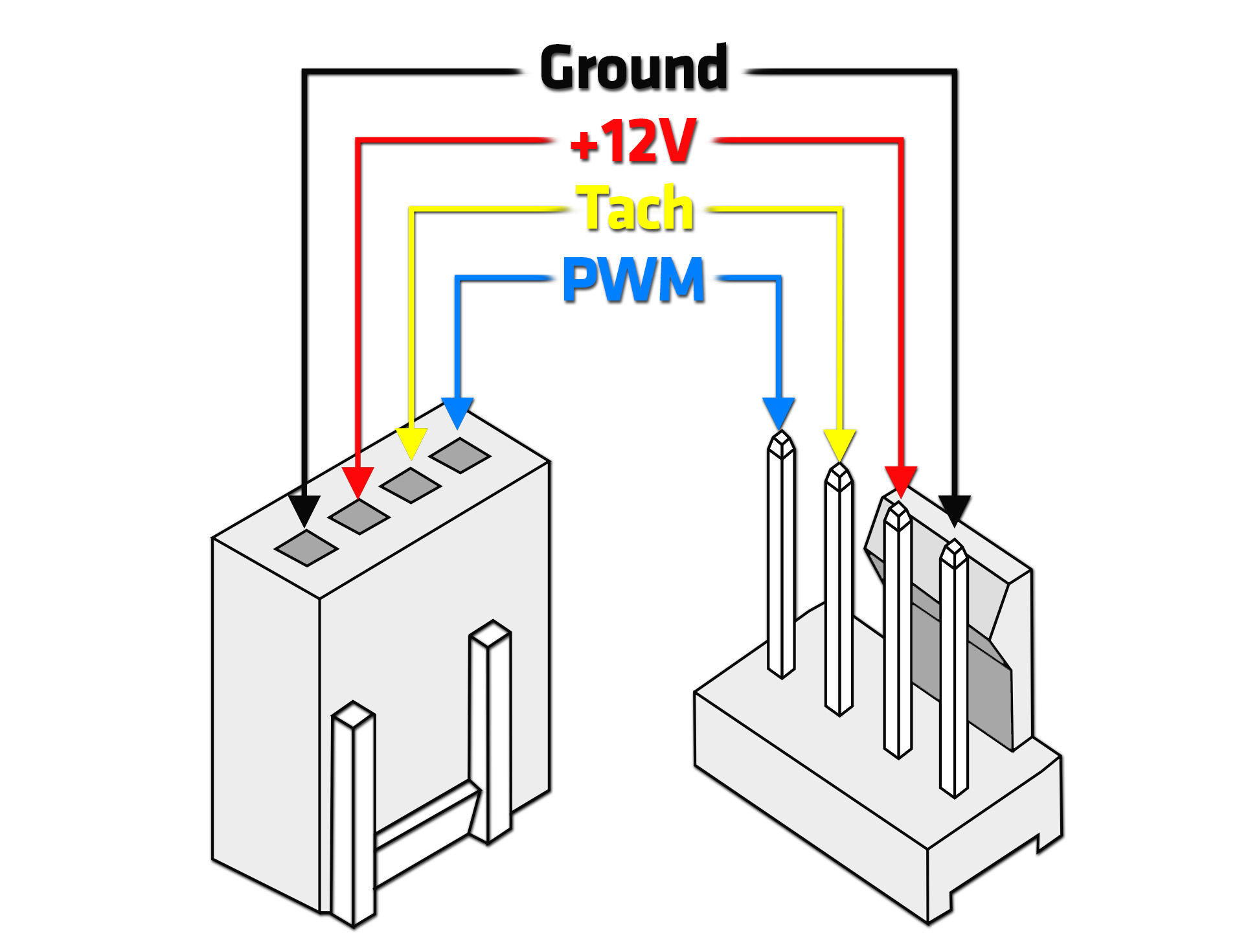
By connecting one or both wires to a different voltage, the voltage the fan receives will be different from the default 12 V the fan was designed for. The voltage a computer cooling fan receives is defined by the difference between the voltage wire (+12 V) and the ground wire (+0 V).
PC 4 PIN FAN PINOUT SERIES
Like other series regulators, the diode will dissipate power equal to its voltage drop times the current passing through it. The voltage drop across the diode will fall with temperature, causing the fan to speed up. The power rating should be noted and some diodes may require cooling to operate at their rated current. A silicon diode provides a relatively constant voltage drop of about 0.7 V per diode data sheets for a specific diode specify its voltage drop, for example the 1N4001 silicon diode's voltage drop varies from approximately 0.7 to 0.9 V as the current varies from 0.01 to 1 A. It is possible to use a rheostat instead.Ī diode in series with the fan will reduce the voltage being output to the fan. For variable fan control, potentiometers could be used along with a transistor such as a MOSFET whose output voltage is controlled by the potentiometer. They need to be of the appropriate power rating. Since the voltage drop is proportional to the current, the fan may not start. Resistors in series with a fan's power pin are the simplest method of reducing fan noise, but they add to the heat generated inside the computer case. There are a few ways to perform this regulation, as described below. By varying the voltage input across the acceptable range for a fan, the speed of the fan will increase (to added voltage) and decrease (to reduced voltage) a faster fan means more air moved and thus a higher heat exchange rate. This control method reduces noise issues and power requirements during periods of low usage, but when the system is operating at capacity, the fan noise can become a problem again.Ī standard cooling fan is a DC motor with blades attached. When the temperature drops below a threshold again, the fans are turned back off. Temperature inside the chassis is checked, and if an outside-of-range temperature is detected, fans are set to their maximum speed. In this style of fan control, the fan is either on or off. Cooling fans equipped with either two- or three-pin connectors are usually designed to accept a wide range of input voltages, which directly affects the rotation speed of the blades. The color of the wires connected to these pins varies depending on the number of connectors, but the role of each pin is standardized and guaranteed to be the same on any system.
PC 4 PIN FAN PINOUT FULL
A variable rotation speed allows the cooling rate to be adjusted to meet demand, quietening the fan and saving energy when full speed is not required. Fan assemblies with this control input provide the ability to adjust the rotational speed of the fan without changing the input voltage delivered to the cooling fan assembly.
PC 4 PIN FAN PINOUT DRIVER
PC 4 PIN FAN PINOUT PC
Since they must move more air through the same area of space, fans will become more noisy.įans installed in a PC case can produce noise levels of up to 70 dB. The byproduct of increased heat generation is that the fan(s) need to move increasing amounts of air and thus need to be more powerful.

Power supplies needed forced cooling, and power supply fans also circulated cooling air through the rest of the PC with the ATX standard. Processors in most early x86-based computers, up to some of the early 486s, did not need active ventilation. Heat production varies with system load, where periods of compute-intensive activity generate much more heat than the idle time does. Computers emit this electrical power as heat generated by all major components.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
